Financial Statements for Banks

Why will the actual amount of money creation be less than the money multiplier predicts? It assumes banks always loan out excess reserves, money is always redeposited into a bank, and consumers do not hold cash. Since those assumptions are far from the reality, the actual changes in the banking system will be much less than the money multiplier indicates. If, instead of a customer deposit, the central bank bought $1000 worth of bonds from a bond dealer (on the open market), things would work a little differently. The bond dealer will deposit the newly created money into their bank account and the excess reserves can be loaned out.

United States Comml Banks: Wkly: sa: Cr: LL: Others: All Oth Loans & Leases (OLL)
These fixed-income securities are created and sold to investors by banks and financial institutions, including government-sponsored enterprises like Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. The Fed owned $2.2 trillion of mortgage-backed securities as of April 24, 2025. That is, they take deposits from customers—individuals or businesses—and use those deposits to finance loans or the purchase of other assets that increase bank earnings and thus profits. Deposits are the largest liability on a commercial bank’s balance sheet. Financial statements for banks present a different analytical problem than manufacturing and service companies. As a result, analysis of a bank’s financial statements requires a distinct approach that recognizes a bank’s somewhat unique risks.
How to read a bank’s balance sheet
- The special characteristics of banking assets and liabilities, largely financial instruments, and the large impact of default alter the traditional approach to solvency.
- Many countries make these data available for researchers and offer the chance of conducting research at the bank level.
- The maximum dollar value of loans would be $9000 ($900 of excess reserves times the money multiplier of 10).
- Some banks, usually smaller banks, also have accounts at larger banks, called correspondent banks.
- By identifying, assessing, and mitigating various risks, banks can safeguard their financial health and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
In the second quarter of 2025, FDIC-insured banks reported $69.9 billion in net income and a return on assets of 1.13 percent. The industry net interest margin was relatively stable, down just 1 basis point from the quarter prior. Asset quality remained generally favorable, and the number of problem banks declined from 63 to 59. In addition to directly lowering long-term interest rates by purchasing long-dated securities, quantitative easing is also intended to signal the central bank’s bias toward looser monetary policy as a further growth spur. The signaling function of quantitative easing has at times ensured that benchmark bond yields rose http://gsp.roeschke.biz/2022/09/23/what-are-expenses-in-accounting-10-types-with/bookkeeping-9/ while the Fed was buying only to drop once the purchase program was discontinued.
- Depending on the current economic environment, the interest rate environment can be beneficial or detrimental to a bank’s profits.
- Really the hard part of this is figuring out how to project these items in the first place which we’re not really doing here.
- The non-performing loan/ loan ratio is used to measure how good a bank’s loan book is.
- The non-performance loan ratio indicates what percentage of loans that are at risk of failing.
- Owner Equity is money (profit) owed to the owners (or shareholders) of the bank.
- And then based on that, and a new deposit number which we’d also probably tie to the loans in some way, we could project everything else on here.
United States Comml Banks: Wkly: Credit
They are categorized into different segments, such as performing loans, non-performing loans, and specific provisions for impaired loans. Assets represent the resources owned by the bank, such as cash, loans, investments, and physical assets. Liabilities represent the bank’s obligations to depositors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
The Federal Reserve Balance Sheet Explained
This allowance exists because they could buy back their own debt in the market, thus reducing their debt for a fraction of its face value. However, critics have pointed out that if a bank doesn’t have the money to buy back its debt, it could still record the reduced value as revenue even though the bank must repay the principal when the debt matures. Nontransaction deposits in depository institutions are now insured to $250,000 by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). For example, a government bond might have a 0% risk weight (very low risk), while a commercial loan might have a 100% risk weight, reflecting the higher risk of default. Cash and cash equivalents refer to the most liquid portion of the bank’s assets, held to meet short-term obligations and provide immediate operational liquidity. We’ll use large financial institutions such as Bank of America and PNC Bank as a reference to explain the components clearly.
Past Quarterly Banking Profiles
- Then you have to think about the interest rates on the Interest-Earning Assets and Interest-Bearing Liabilities and calculate Interest Income or Expense.
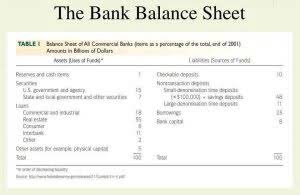
- On a bank balance sheet, assets always equal liabilities (they balance).
- Note that line item 1, Bank credit, and line item 9, Loans and leases in bank credit, no longer include Fed funds and reverse RPs with nonbanks and the category Interbank loans (former line item 31) has been eliminated.
- Liabilities are either the deposits of customers or money that banks borrow from other sources to use to fund assets that earn revenue.
- Average balances provide a framework for the bank’s financial performance.
- This comparison helps us understand if the bank has sufficient funds to meet future contingencies.
If we add total liabilities and shareholders’ equity, we will get a number that should match the total assets. Other Deposits (sometimes listed as “savings deposits”) are deposits from customers that go into non-checking accounts. If a customer makes a deposit into their savings account, other deposits will increase (excess reserves will also increase). Excess reserves will decrease whenever loans are made, securities are purchased, physical assets are purchased, or any of the liabilities are decreased. Required reserves only change when there is a change in the amount of demand Mental Health Billing deposits (checkable deposits). They always equal a percentage (set by the central bank’s reserve requirement) of checkable deposits.
View Nepal’s Nepal Commercial Banks: Annual: Deposit: Current: Foreign from 1960 to 2017 in the chart:
We got to our Net Change in Cash, and then we went back and linked in everything properly on the Balance Sheet. When you link a bank’s financial statements, you always start with the Loans, Deposits, and the Key Interest-Earning Assets and Interest-Bearing Liabilities. So in this case, we started by looking at the Balance Sheet and keeping many of these items almost the same, except we did assume some loan additions here which did change things a little bit. The adoption by some banks of FAS 159, The Fair Value Option forFinancial Assets and Financial Liabilities (FVO), affected commercialbank balance sheet data for April 2, 2008.

The Federal Reserve System is the central bank of the United States and conducts the nation’s monetary policy. The primary goals of the Fed’s monetary policy are to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. To complete the balance sheet of a regular company, we have only one thing left. By adding the “current liabilities” and “non-current liabilities,” we will get “total liabilities.” However, what separates the bank from the other regular company is that the bank takes more risk than any regular company. Bank Balance Sheet is prepared differently from the Company Balance Sheet.

- Loans from the central bank are considered liabilities, much like normal debt.
- The balance sheet of a regular company is similar to a simple balance sheet format.
- Credit risk arises when a bank makes a loan to an individual or company.
- Deposits are the largest liability on a commercial bank’s balance sheet.
- Physical Assets include the bank building, desks, chairs, computers, and even those pens with the chain attached.
Moreover, banks use the average balance for their balance sheets, which is unique if we compare it with the regular company operations. If you look at a balance sheet of a regular company, you will have a surface-level idea about how a balance sheet works. For example, the bank’s balance sheet is arranged similarly, but the items under the heads are different.
Memoranda line items 45, 46, 47, and 48, covering securitized consumer and real estate loans, will also be dropped. Memoranda line items 45, 46, 47, and 48, covering securitized consumer and real estate loans, have also been dropped. Previous line items 35 and 44, Trading assets and liabilities, respectively, are no longer being published. The amount of trading assets and liabilities are now reported as part of other assets and liabilities (line items32 and 39), respectively. As a last resort banks can also borrow from the Federal Reserve (Fed), though they rarely do this since it indicates that they are under financial balance sheet of a commercial bank stress and unable to get funding elsewhere.
